A new Google-Ipsos report shows AI adoption is increasing globally, especially in emerging markets.
However, the study reveals challenges like regional divides, gender disparities, and slower adoption in developed countries.
Critics, including Nate Hake, founder of Travel Lemming, point out how Google overlooks these challenges in its report coverage.
Takeaways of Google’s AI Ipsos survey when you look through the PR spin 👓👇
1) 71% of Americans did not even use Generative AI in 2024
2) 58% of Americans think AI is unlikely to benefit them
3) There is a concerning gender gap in AI usage
4) US society is deeply apprehensive… https://t.co/dSZEtXsDoG— Nate Hake (@natejhake) January 16, 2025
While optimism around AI is rising, it’s not resonating with everyone.
Here’s a closer look at the report and what the numbers indicate.
AI Is Growing, But Unevenly
Globally, 48% of people used generative AI last year, with countries like Nigeria, Mexico, and South Africa leading adoption. These regions also show the most excitement about AI’s potential to boost economies and improve lives.
Adoption lags at 29% in developed nations like the U.S. and Canada, meaning that 71% of people in these regions haven’t knowingly engaged with generative AI tools.
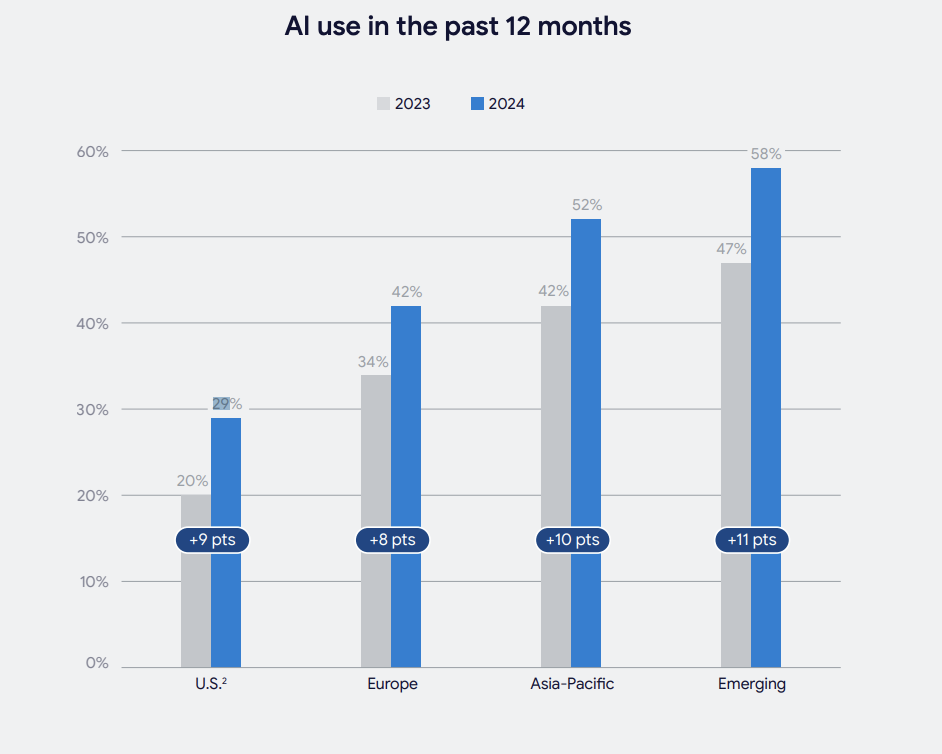 Screenshot: Google-Ipsos Study ‘Our life with AI: From innovation to application,’ January 2025.
Screenshot: Google-Ipsos Study ‘Our life with AI: From innovation to application,’ January 2025.Optimism Outweighs Concerns
Globally, 57% of people are excited about AI, compared to 43% who are concerned—a shift from the year prior, when excitement and concerns were evenly split.
People cite AI’s potential in science (72%) and medicine (71%) as reasons for their optimism. Respondents see opportunities for breakthroughs in healthcare and research.
However, in the U.S., skepticism lingers—only 52% believe AI will directly benefit “people like them,” compared to the global average of 59%.
Gender Gaps Persist
The report highlights a gender gap in AI usage: 55% of global AI users are men compared to 45% women.
The disparity is even bigger in workplace adoption, where 41% of professional AI users are women.
Emerging Markets Are Leading the Way
Emerging markets are using AI more and are more optimistic about its potential.
In regions like Nigeria and South Africa, people are more likely to believe AI will transform their economies.
Meanwhile, developed countries like the U.S. and U.K. remain cautious.
Only 53% of Americans prioritize AI innovation, compared to much higher enthusiasm in emerging markets.
Non-Generative AI
While generative AI tools like chatbots and content generators grab headlines, the public is more appreciative of non-generative AI applications.
These include AI for healthcare, fraud detection, flood forecasting, and other practical, high-impact use cases.
Generative AI, on the other hand, gets mixed reviews.
Writing, summarizing, or customer service applications don’t resonate as strongly with the public as AI’s potential to tackle bigger societal issues.
AI at Work: Young, Affluent, and Male-Dominated
AI is making its way into the workplace. 74% of AI users use it professionally for writing, brainstorming, and problem-solving tasks.
However, workplace AI adoption is skewed toward younger, wealthier, and male workers.
Blue-collar workers and older professionals are catching up—67% of blue-collar AI users and 68% of workers aged 50-74 use AI at work—but the gender gap remains pronounced.
Trust in AI Is Growing
Trust in AI governance is improving, with 61% of people confident their governments can regulate AI responsibly (up from 57% in 2023).
72% support collaboration between governments and companies to manage AI’s risks and maximize its benefits.
Takeaway
AI use is growing worldwide, though many people in North America still see little reason to use it.
To increase AI’s adoption, companies must build trust and clearly communicate the technology’s benefits.
For more details, check out the full report at Google Public Policy.
Featured Image: Stokkete/Shutterstock
